If you’ve ever wanted to dive into engineering simulations, scientific computing, or data analysis, MATLAB is one of the most powerful tools you can use. This MATLAB software tools guide is designed to walk you through everything you need to know—from its basic interface to advanced toolboxes and applications—in a clear, step-by-step manner.
Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, this guide will make MATLAB easy to understand and use.
What is MATLAB?

MATLAB, short for Matrix Laboratory, is a high-level programming environment designed for numerical computation, visualization, and algorithm development. Unlike general-purpose programming languages, MATLAB is optimized for matrix and vector computations, making it perfect for:
- Engineering simulations
- Data analysis and visualization
- Algorithm development
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence
- Scientific research and academic projects
MATLAB combines a programming language with a user-friendly environment, interactive tools, and specialized toolboxes for specific tasks. It is widely used in universities, research labs, and industries like aerospace, finance, robotics, and healthcare.
The MATLAB Desktop: Your Command Center
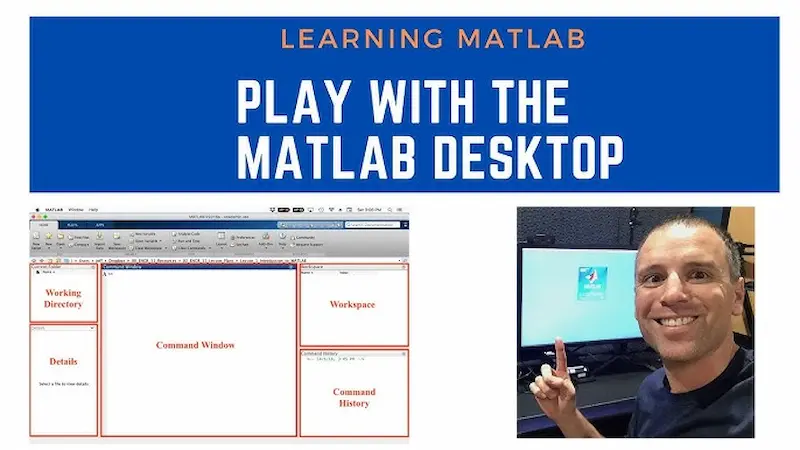
When you first open MATLAB, the Desktop Environment is what you see. It’s designed to make coding, debugging, and data analysis simple.
Key Components:
- Command Window
- This is where you type MATLAB commands and see immediate results.
Example:
x = 5;
y = x^2;
disp(y)
- Output: 25
- Workspace
- Displays all the variables currently in memory. You can view, edit, or delete variables here.
- Example: After running the code above, x and y appear in the workspace with their values.
- Displays all the variables currently in memory. You can view, edit, or delete variables here.
- Command History
- Keeps track of all commands you’ve entered. You can reuse or modify previous commands without retyping them.
- Keeps track of all commands you’ve entered. You can reuse or modify previous commands without retyping them.
- Current Folder
- Shows files in your working directory. It helps you organize scripts, functions, and data files.
MATLAB Editor: Writing Scripts and Functions
The MATLAB Editor allows you to create .m files (scripts and functions) for tasks that require multiple commands.
Features of the MATLAB Editor:
- Syntax Highlighting: Makes your code easier to read.
- Debugging Tools: Set breakpoints, step through your code, and watch variables.
- Live Scripts: Combine code, formatted text, and output in a single interactive document.
Example of a simple function:
function result = addNumbers(a, b)
result = a + b;
end
Call it in the Command Window:
sum = addNumbers(3, 7);
disp(sum)
Output: 10
Simulink: Graphical System Modeling
Simulink is a graphical programming environment integrated with MATLAB. It allows you to model, simulate, and analyze dynamic systems without writing complex code.
Use Cases:
- Control systems for robots or vehicles
- Signal and image processing
- Real-time simulations in aerospace or mechanical engineering
Simulink uses block diagrams, where you drag and connect blocks representing mathematical operations, inputs, outputs, and feedback loops. It’s intuitive for visual learners and engineers who prefer diagram-based modeling.
You may also like to read this:
Latest Academic MATLAB Research News And Updates 2025
Latest Engineering Research Updates 2026 You Can’t Miss – MATLAB News
MATLAB Research Papers Explained – Complete Guide
Current MATLAB Scientific Research: Key Insights & Trends
Exploring New Discoveries MATLAB Applications In 2025
MATLAB Toolboxes: Specialized Functions for Every Field
Toolboxes are collections of functions and apps designed for specific applications. They expand MATLAB’s capabilities and make complex tasks simple.
Popular MATLAB Toolboxes:
- Signal Processing Toolbox – Analyze, filter, and visualize signals like audio or sensor data.
- Image Processing Toolbox – Enhance, segment, and manipulate images. Ideal for computer vision projects.
- Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox – Perform data analysis, clustering, regression, and predictive modeling.
- Deep Learning Toolbox – Build, train, and deploy neural networks.
- Optimization Toolbox – Solve linear, nonlinear, and constrained optimization problems.
- Control System Toolbox – Design and analyze control systems using MATLAB and Simulink.
MATLAB App Designer: Build Interactive Apps
MATLAB App Designer lets you create professional graphical user interfaces (GUIs) without extensive programming knowledge. You can:
- Drag and drop UI components like buttons, sliders, and tables.
- Connect UI elements to MATLAB code.
- Make apps that are interactive for users or for presentations.
Example: You can create a simple calculator app that adds two numbers when the user clicks a button.
MATLAB Live Editor: Interactive, Dynamic Coding
The Live Editor allows you to create interactive scripts combining code, formatted text, and visualizations. Key features include:
- Displaying outputs immediately next to the code
- Adding headings, images, and LaTeX equations
- Interactive controls like sliders and dropdown menus
Example: Create a plot of a sine wave with adjustable frequency using a slider—changes update instantly without rerunning the script manually.
MATLAB Online & MATLAB Drive
MATLAB Online is the cloud version of MATLAB. With it, you can:
- Access MATLAB in any browser without installation
- Store projects and scripts in MATLAB Drive (cloud storage)
- Collaborate with teammates remotely
This is particularly useful for students or teams working across multiple locations.
Practical Tips for Using MATLAB Efficiently
- Vectorization Over Loops – MATLAB is optimized for matrix and vector operations. Replace loops with vectorized operations to speed up code.
- Use Breakpoints for Debugging – Step through your code to find and fix errors effectively.
- Leverage Built-in Functions – MATLAB has thousands of functions for math, statistics, plotting, and more.
- Organize Your Projects – Keep scripts, functions, and data files organized in folders.
- Explore Examples – MATLAB provides extensive examples for all toolboxes. Try them to understand functionality.
Why MATLAB is a Preferred Choice
- Intuitive Interface: Combines coding, visualization, and GUIs.
- Extensive Toolboxes: Covers nearly every technical field.
- Visualization Power: Create interactive 2D and 3D plots, dashboards, and animations.
- Integration: Works seamlessly with Python, Java, C/C++, and hardware like Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
- Industry Standard: Widely used in academia, research, and industry projects.
Conclusion
This MATLAB software tools guide has provided a comprehensive overview of MATLAB’s desktop environment, editor, Simulink, toolboxes, App Designer, Live Editor, and online features. MATLAB is more than a programming platform—it’s an ecosystem that allows you to perform complex computations, visualize data, and build interactive applications.
By exploring its tools and features step-by-step, you can maximize efficiency, learn faster, and take your projects to the next level.
With consistent practice, MATLAB can become your go-to tool for scientific computing, engineering design, and data analysis. Start experimenting with the commands, scripts, and toolboxes today, and you’ll quickly see why MATLAB is trusted by millions worldwide.
FAQs
1. What is MATLAB used for?
MATLAB is used for numerical computing, algorithm development, data analysis, and visualization. It is widely applied in fields like engineering, physics, finance, robotics, machine learning, and scientific research. You can perform complex calculations, create interactive plots, and even build apps using MATLAB.
2. What is the difference between MATLAB and Simulink?
MATLAB is a programming environment for numerical computation, data analysis, and algorithm development
Simulink is a graphical environment integrated with MATLAB for modeling, simulating, and analyzing dynamic systems using block diagrams.
Think of MATLAB as the coding engine and Simulink as a visual design tool for system modeling.
3. What are MATLAB toolboxes?
Toolboxes are specialized collections of functions and apps designed for specific tasks. Examples include:
ignal Processing Toolbox – for analyzing and filtering signals
Image Processing Toolbox – for manipulating images
Deep Learning Toolbox – for building and training neural networks
They extend MATLAB’s core functionality, making complex tasks much easier.
4. Is MATLAB easy to learn for beginners?
Yes! MATLAB is beginner-friendly because of its interactive desktop, live editor, and extensive documentation. Start with basic commands and gradually explore toolboxes and Simulink. Many online tutorials and examples are available to help beginners learn quickly.
5. Can I use MATLAB without installing it?
Yes. MATLAB Online allows you to use MATLAB directly in a web browser. Additionally, MATLAB Drive provides cloud storage so you can access your scripts and projects from anywhere.